- Who are investors in the Indian Debt Market?
The institutional investors who invest in the Indian Debt Market are:
- Banks
- Insurance Companies
- Provident Funds
- Mutual Funds
- Trusts
- Corporate Treasuries
- Fixed Deposits
- Foreign Investors
- Primary Dealers (Retail participation allowed, though currently muted)
Retail investors are allowed to invest in select issuances though their participation is in evolving phase.
- Who Regulates Indian G-secs and Debt Market?
Money Market and Government Securities markets are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Whereas, other fixed income instruments (PSU bonds, Non-Convertible Debentures, etc.) are regulated by both, RBI and SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India).
- What is yield to maturity (YTM)?
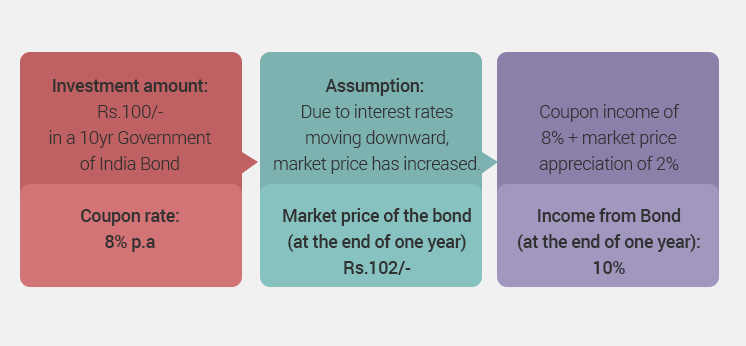
The Yield to maturity (YTM) is the internal rate of return earned by an investor assuming that the bond will be held until maturity, and that all coupon and principal payments will be made on schedule. It basically measures the total income earned by the investor over the entire life of the security.
This total income consists of three components:
- Coupon income: The fixed rate of return that accrues from the instrument.
- Interest-on-interest at the coupon rate: Compound interest earned on the coupon income.
- Capital gains/losses: The profit or loss arising at redemption/maturity of the security. (Difference between the purchase price and the proceeds received on redemption/maturity).
- What are the Open Market Operations (OMOs)?
OMOs is a tool used by the Reserve Bank of India to adjust the rupee liquidity conditions in the market. When the RBI feels there is excess liquidity in the market, it resorts to sale of securities thereby sucking out the rupee liquidity. Similarly, when the liquidity conditions are tight, the RBI will buy securities from the market, thereby releasing liquidity into the market.
- What does the credit rating for bonds mean?
Various credit rating agencies evaluate the credit worthiness of entities issuing debt instruments. This rating helps investors to make an informed decision before investing in any debt instrument.
The rating is given as an alphanumeric code that represents a graded structure or creditworthiness. Private independent rating services such as CRISIL, ICRA, CARE, and FITCH provide these evaluations.
Few ratings and their implications:Rating Rank Implication AAA Rating Highest credit rating Implies a high credit quality and a small chance of default D (for default) Lowest credit rating Implies a very risky investment - What are the different types of instruments in fixed income?
Few of the common fixed income instruments are:
- Government Securities (G-secs)
- State Development Loans (SDLs)
- Corporate Bonds
- Treasury Bills
- Commercial Paper
- Certificate of Deposits
- Fixed Deposits
- Inflation Indexed Bonds
- What are fixed income securities?
A fixed income security is issued by Government, corporates or other entities. The security represents a loan that is offered by an investor to an entity. As the name suggests, a fixed income security offers fixed periodic interest (known as coupon payment) to the investor.
- How does the trading in Government securities (G-secs) take place?
There is an active secondary market (for purchasing securities from other investors) in G-secs. The securities can be bought / sold by investors in the secondary market either:
- Over the Counter (OTC) or
- Through the Negotiated Dealing System-Order Matching (NDS-OM).
- What factors determine interest rates?
Few of the factors which govern interest rates are:
- Monetary Stance of RBI
- Inflation Rate
- Liquidity in the Banking system
- Government Borrowings
- Corporate Borrowing Requirements
- Global Interest Rates
- Stability of Currency Markets
- What is Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF)?
LAF is offered by RBI to scheduled commercial banks and primary dealers for liquidity management on a day to day basis. Under LAF, these banks and dealers can approach RBI:
- For funds in case of requirement, or
- Park excess funds when not required
This facility is available on an overnight basis, against the collateral of Government securities including State Government securities.
- What is accrued interest on a bond?
The accrued interest on a bond is the amount of interest accumulated on a bond since the last coupon payment (interest payment). The interest has been earned, but because coupons are paid only on coupon dates, the investor has not gained the money yet. In India, day count convention for G-secs is 30/360.
- What is a yield curve?
A yield curve is a line that plots the interest rates on Y-axis and maturity dates on X-axis. The shape of the yield curve gives an idea of future interest rate change and economic activity.
Type of Yield Curve Feature Implication Normal Longer maturity bonds have a higher yield compared to shorter-term bonds Risks associated with time Inverted Shorter-term yields are higher than the longer-term yields A sign of upcoming recession Flat (or humped) Shorter- and longer-term yields are very close to each other A predictor of an economic transition - Why invest in fixed income securities?
Fixed income investments are a secure and low-risk way to generate a steady flow of income. Investment in fixed income securities should be an important part of a well-diversified portfolio.
- How is yield related to price?
If interest rates or market yields decline, the price of a bond rises. Conversely, if interest rates or market yields rise, the price of the bond falls. In other words, the yield of a bond is inversely related to its price.
- What is Duration?
Duration is the payback period of a bond to break even, i.e., the time taken for a bond to repay its own purchase price. Duration is expressed in number of years. Duration is useful primarily as a measure of the sensitivity of a bond's market price to interest rate (i.e., yield) movements. It is approximately equal to the percentage change in price for a given change in yield.
Digilocker FAQ
-
Through which URLs can I access DigiLocker?
DigiLocker, the National Digital Locker System launched by the Government of India can be accessed using the below URLs:
-
Which benefits do I get from using DigiLocker?
- Citizens can access their digital documents anytime, anywhere and can also share them online. This makes it convenient and time-saving
- It reduces the administrative overhead of Government departments by minimizing the use of paper
- It makes it easier to validate the authenticity of documents as they are issued directly by the registered issuers
-
How can I sign up for DigiLocker?
- Open the DigiLocker website www://digilocker.gov.in OR download DigiLocker application from Google Play Store/ iOS App Store
- Click on the Sign-up button and fill in mandatory information as below :
- Full Name (as per Aadhaar) – Mandatory
- Date of Birth (as per Aadhaar) – Mandatory
- Gender – Mandatory
- Mobile Number – Mandatory
- Set 6 Digit Security Pin – Mandatory
- Email ID – Optional
- Aadhaar Number – Optional (DigiLocker uses Aadhaar to verify the identity of the user and also enables authentic document access)
- Your mobile number will be authenticated by sending an OTP (one-time-password) followed by selecting a username & password. This will create your DigiLocker account.
- After your DigiLocker account is successfully created, you can voluntarily provide your Aadhaar number (issued by UIDAI) to avail of additional services.
-
How can I get my Policy Document added to DigiLocker? If I have already signed up.
Here are the steps (if you have not linked Aadhaar to your DigiLocker account):
- Login to DigiLocker with your credentials
- Upon login, you will see a dialogue box with a message to get your eAadhaar
- Click on the “Click here” link. An OTP box will appear in the dialogue
- You will receive an OTP on your mobile number linked to Aadhaar. Enter this OTP in the OTP box and click ’Verify OTP’ button
- On successful validation of the OTP, you will be redirected to the ’Issued Document’ page where URI for eAadhaar will be listed
- Click on the ’Save’ icon next to Aadhaar Card on the ’Issued Document’ page. Your eAadhaar will then be saved to the “Uploaded Document” section
- Go to Home and click on Banking & Insurance Section (View All) and look for Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Ltd
- Click on “Policy Document”
- The screen will show the Aadhaar Name and Date of Birth registered in Aadhaar Records
- Type in your Policy Number and click on the ‘Get Document’ button
- On successful validation of the Policy Number and Proposer Date of Birth, you will be redirected to the ’Issued Document’ page where URI for e-Policy will be listed
- Click on the “Save” icon next to Policy Document on the ’Issued Document’ page. Your e-Policy will be saved to the “Uploaded Document” section
Here are the steps to get e-Policy in DigiLocker (if you have linked Aadhaar to your DigiLocker account):
- Login to DigiLocker with your credentials
- Click on Banking & Insurance Section (View All) and look for Future Generali India Life Insurance Company Ltd.
- Click on “Policy Document”
- Type in your Policy Number and click on Get Document Button
- On successful validation of the Policy Number and Proposer Date of Birth, you will be redirected to the ’Issued Document’ page where URI for ePolicy will be listed
- Click on the ’Save’ icon next to Policy Document on the “Issued Document” page. Your e-Policy will be saved to the ’Uploaded Document’ section.
-
I would like to understand more about Digilocker
Please visit https://digilocker.gov.in/faq.html





